Wheel Alignment
|
Wheel alignment is the position of the wheels relative to your car. When properly aligned, the wheels point in the right direction. Without proper alignment, the wheels resist your steering commands, as well as each other. Alignment also affects gas mileage and tire wear. If your tires are pointed in different directions, they fight against each other and can cause tread wear.
|
Computerized alignment equipment is used to measure all alignment angles on today's cars. These include both adjustable and non-adjustable angles. (Non-adjustable angles require repair or replacement of the suspension component.) The most common adjustable angles are:
Toe |
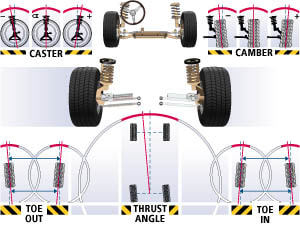
This refers to the tilted direction of the wheels toward or away from one another when viewed from the top. Toe is the most critical tire wearing angle. Tires that "toe-in" point toward one another. Tires that "toe-out" point away from each other.
|
Camber |
This refers to the tilt of the wheels toward or away from one another when viewed from the front. Wheels that tilt in toward the vehicle have "negative camber." Wheels that tilt away from the vehicle have "positive camber."
|
Caster |
This refers to the angle of the steering axis in relation to an imaginary vertical line through the center of the wheel when viewed from the side. "Positive caster" is the term used when the vertical line is tilted back toward the rear. If it's tilted forward, we call it "negative caster." The proper caster angle stabilizes your car for better steering.
|
Thrust Angle |
This refers to the relationship of all four wheels to each other, as well as their relationship to an imaginary center line that runs from bumper to bumper. The term "thrust line" refers to the direction in which the rear wheels are pointed. Thrust angle is correctable on cars with adjustable rear suspensions. If your car has a non-adjustable suspension, thrust angle is compensated for by aligning the front wheels to the rear wheels.
|